Parents must pay great attention to their children's physical development in order to adjust their shortcomings in a timely manner.Valve deformation of children's feet is a common pathology.Although the defect is congenital or acquired, the diagnosis, prevention and correction methods are similar.
What is a valgus and a flat foot
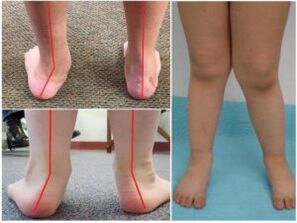
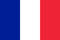
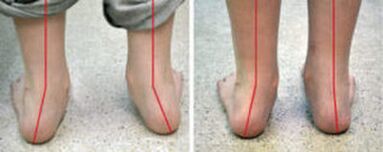
Doctors outside the term indicate any joint curvature from inside the conditional intermediate line (axis), where the obvious "X-shaped" deviation is obvious.The most obvious example in pathology is the bones on the thumb (only outside the operating room).The valgus deformation abbreviated as "flip-out foot" (the sun) is an incorrect setting on horizontal support.If a -age baby puts his legs together, the back is obvious due to the movement of the inner ankle toward the opposite limb, and the heel is off the outside.Meanwhile, a flat child relies primarily on the inner (internal) part of the feet.Therefore, the sole of the foot is “looked.”A variety of diseases are flat feet (PVS).It combines flat feet and X-shaped curvature.In infants, the collection of feet gradually flattens out in addition to deformation.
Extraverted curvature degree
The stage of ignoring pathology depends on the magnitude of the skew angle between the heel and the median axis.
There are 4 diseases:
- I-up to 15°;
- II -15-19°;
- iii -20 to 20-29°;
- IV -30° or more.
1-2 peripheral deformation stages can be eliminated by conservative methods.At 3 degrees, extended treatment is required.During 4 stages, surgical correction may be required.
Causes of deformation
There are three factors, so the foot has curved: impaired intrauterine development, chronic physical overload, and diseases of the musculoskeletal system.These factors weaken ligaments, tendons, muscles, so the foot is not fixed in normal anatomical position.
The reason for the acquisition of the tilt, Pinvalgus Foot (code M21.0 in ICD-10):
- Leg setting is premature when the baby’s joints are not ready to address such loads;
- "Wrong" shoes (narrow heels are narrow, no supplier).
- Muscle hypotension, congenital muscle distribution;
- Heavy weight, obese;
- rickets;
- Neuromuscular diseases (polio, cerebral palsy in children, polyneuropathy with various causes);
- congenital dislocation of the hip thigh and dysplasia;
- Trauma in the foot or lower leg;
- Flake's plaster, instructor or pillow to keep the long-term fixation of the legs.
The congenital origin of the coat and flattening of the foot structure - Volgus defect (Q66.6 code in ICD-10) may be due to a abdominal injury or genetic disease transferred by pregnant women.This curvature can be seen immediately after birth, sometimes manifesting before the baby starts walking.
How to determine the stop deformation
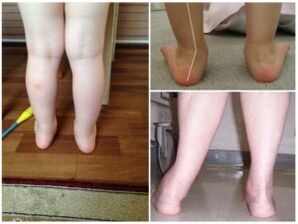
Changes in the configuration of the lower limbs are set along the axis of the legs.This is the name of the traditional line, from the center of the hip joint through the knee, the ankle joint to the middle of calcium.The specification means the passage of the axis through the center of the joint, which should not be moved from the right or to the left.
feature
In newborns, which have the innate nature of valgus, can be found immediately or in the first few months of life.In most cases, a year and a half later, there are signs of children's defects in going out.The baby's behavior and gait can suspect the existence of the disease.Most commonly, the following general symptoms of pathology are found:
- Improved flexibility of small joints;
- Reduce the height of the sole;
- displacement of the center of gravity (when trying to walk, the child only relies on the inside of the foot, and its outer edge will rise slightly);
- Uncertain gait;
- Fast physical fatigue, need rest and let the baby relax;
- Complaints about leg pain regularly and are unwilling to walk;
- Swelling and redness of the skin on the feet and ankles;
- The shoes are not evenly dressed and are expressed more from the inner edge of the sole.
Methods to identify deformations
The method of diagnosis of defects involves the orthopedic examination of the infant's foot, followed by the infant's instructions for instrumental examination.In three predictions, he was made into X-rays to find out the extent of bone displacement.They also performed planetary techniques to determine the height of the toes and the severity of the flat feet.Using a column-meter, calculate the center of the sole pressure.This is an effective diagnostic method because it allows you to recognize valgus deformation at an early stage.Sometimes, to clarify the results of the examination, an ultrasound examination may be performed.The visual sign of pathology is the sole, which turns slightly along the side and moves along the side, lifting outward from the middle line.As the flat deformation was deformed, the vault disappeared and the feet became flat.To rule out the neurological causes of the defect, orthopedics point the child to a specialist with a narrowing.
Calibration method
To eliminate extroversion, the main task is to give the right position of the foot and subsequently strengthen the ligaments attached to the heel and muscle tendons.
Fix joints in a conservative manner
Use natural defects, use gypsum dressings or counselors.The purpose of fixing the foot at the correct angle is to eliminate curvature by fixing it.Although ossification has not been completed, the fabric is elastic and therefore vulnerable to this correction.With the aid of the tilt defect after obtaining, orthopedic shoes are given to the child in order to restore the correct setting of the foot.No discomfort should be caused during use.A special shoe insole has a super size with a lateral stiffness, a soft pillow under the dome under the foot (Pelot).It is also recommended to wear this kind of shoes during post-operative recovery to consolidate treatment outcomes.
Various insoles
Experts recommend ordering orthotics, shoes or insoles for children in orthopedic salons based on the various sizes and castings of the feet.The price of the product will be slightly higher, but the use will bring more obvious results.
Strengthen small joints
For general hardening and nourishing muscles in the lower limbs, a contrasting foot bath is recommended.To do this, the feet are alternately immersed in containers with cold and hot water.They start with the liquid at a temperature of 36°C and then change the value to 1°C every week.
It is useful to do the following exercises:
- Instead walk on socks, high heels, inside, outside edges;
- Collect small objects, grab fabric or paper, and draw with the fingers of your feet;
- Slide the ball on the floor;
- a set of movements of fingers (bending, reproduction and closure);
- Walking on pebbles, the surface is not flat.
Orthopedics can prescribe massage classes for the lumbar spine, which are affected by the lower limbs or both legs.It is best to do it after heating with paraffin or Ozokerritic.The muscles on the surface of the legs are affected by supplement massage exercises (pat, kneading).The outer surface of the legs should be massaged according to relaxation techniques - caressed, rubbed.
Physical Therapy Procedures
If the deformation of the foot causes inflammation of the joint structure, the tendons of the muscles are prescribed with electrophoresis with painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs, magnetic therapy, black wax, paraffin and therapeutic mud.For selective muscle stimulation, a bimodal current is used.
Surgical treatment
In early childhood, no fundamental treatments are used.However, if the defect interferes with normal walking, then operate on the young child.During the surgical intervention, doctors using metal elements (titanium wire, screws, plates) secured the deformed joints in normal positions.The surgeon can also strengthen the joints by moving the tendon of the fibula or extending the Achilles tendon.Following these procedures, rehabilitation includes the use of orthopedic products, massage, physical therapy, and physical therapy exercises.
Preventive measures
To prevent the extroverted deformation of your feet, you need to buy children's comfortable shoes corresponding to the size of your legs, i.e. the anatomy of your feet.How to choose - watch the recommendations of E.O. Komarovsky at the video. Doctors say that this is a frequent violation in children and helps to form the feet correctly until they are 12 years old.The teenager is likely to need surgery to correct obvious defects in his foot.The child should walk barefoot on sand, grass, walk a lot, eat fully. Dosed sunbathing prevents ribets in children, which is one of the causes of the disease. Physical education, hardening of the body, regular courses of general strength massage. Gymnastics for the muscles of the foot is also important, including the creation of a pattern of a leg in the sand. Active outdoor games, swimming also contribute to strengthening the muscles and ligaments of thelower extremes. All these measures prevent the development of foot defects. The joints and bones of the lower limbs are not strengthened.A planned examination by a pediatrician and a stenosis specialist who missed the plan is unacceptable, allowing you to identify pathology early.
Doctor's answer to parents
How to warn of congenital valgus deformation?Unfortunately, the bad habits of the development of the musculoskeletal system cannot be prevented.Even if they do not find any deviation in the hospital, babies should check in regularly, receive massages, and walk barefoot on uneven but safe leg surfaces.At home, massage carpets are recommended.Obtaining high-quality shoes also helps keep the feet in the right position and form a set of physiological heights.This prevention will prevent even congenital foot turnaround from progressing.
Which doctor treats pathology?
If necessary, the pediatrician points the baby to the pediatric orthopedic, trauma scientist, surgeon.
What is the change foot?
The variation deviation is the displacement of the inner line of the heel bone.In this case, the collection of the feet is very high and the pressure center is moved to the outer edge of the sole.The defect was treated in the same way as the valgus deformation, and the skew angle was adjusted only from the other side of the foot.
Velveolar deformation of children's feet: consequences and corrections
The valgus deformation of the foot is a pathological change in the musculoskeletal system, where the height of the foot is reduced and the axis of the lower limbs is moved.
Defects can be congenital and can also develop during childhood, leading to flat feet, posture violations and other health problems.Usually, it is conservatively adjusted during the long-term treatment of charging, massage, and physical therapy.By performing deformation work regularly, you can achieve proper legs and confident gait.
Flat deformation of feet in children's symptoms
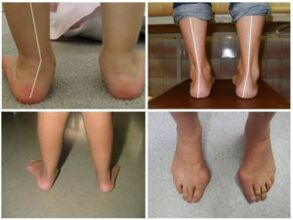
This leg defect can be identified by the following external signs:
- The inner ribs are scattered with the feet and the child is lying inside the feet.
- Heels and fingers deploy externally;
- The middle part of the foot is flat or significantly lowered;
- When reducing knees, the legs gain an ix eyebrow shape, the legs do not fuse together, and the distance between them is about 4-5 cm.
- Uncertain, clumsy gait, the child is often stuck and radiates;
- The kid took a walk very quickly.
When can defects be manifested?
From the moment the baby tries to take his first step, the arch of the foot begins to form.For babies, flat feet are considered the norm.When performing vertical positions independently, children develop musculoskeletal system, "habiting" them to new functions.The bones and ligaments begin to experience the load, the foot is strengthened and takes the correct anatomical shape.This usually occurs for up to 1.5 years.If the vault at this age remains flat, there is no bending formed, which the doctor defines as a valgus deformation of the foot.Usually, violations are found during a physical examination, but if the parent independently notices the above signs, contact orthopedics immediately is required.If you start adjusting early, the recovery is faster and there are no serious consequences.
in conclusion
Parents need to spend the maximum time preventing defects in infants’ physical development, including gymnastics, massage classes and other recreational activities.If valgus deformation of children's feet is not eliminated through conservative treatment, you need to agree to surgical intervention to correct the shape of the feet.After all, the development of advanced pathology, the development of spinal disease and limb shortening.